A macular hole is a small break in the macula, the part of your eye responsible for detailed, central vision.
The macula is a very small area at the center of the retina — a thin layer of light-sensitive tissue that lines the back of the eye. Light rays are focused onto the retina, where they are transmitted to the brain and interpreted as the images you see. It is the macula that is responsible for your pinpoint vision, allowing you to read, sew or recognize a face.
As we grow older, the thick vitreous gel in the middle of our eyes shrinks and pulls away from the macula. If the gel sticks to the macula and doesn’t pull away, the macular tissue stretches and eventually tears, forming a hole.
If you have macular hole symptoms, you will have blurred and distorted central vision.
WHAT CAUSES A MACULAR HOLE ?
Your eye is filled with a gel-like substance called vitreous, which lies in front of the macula. As you age, the vitreous gel shrinks and pulls away from the macula, usually with no negative effect on your sight. In some cases, however, the vitreous gel sticks to the macula and is unable to pull away. As a result, the macular tissue stretches. After several weeks or months the macula tears, forming a hole.
Macular holes are associated with aging and usually occur in people over the age of 60. Less common causes of macular holes include injury to the eye and long-term swelling of the macula.
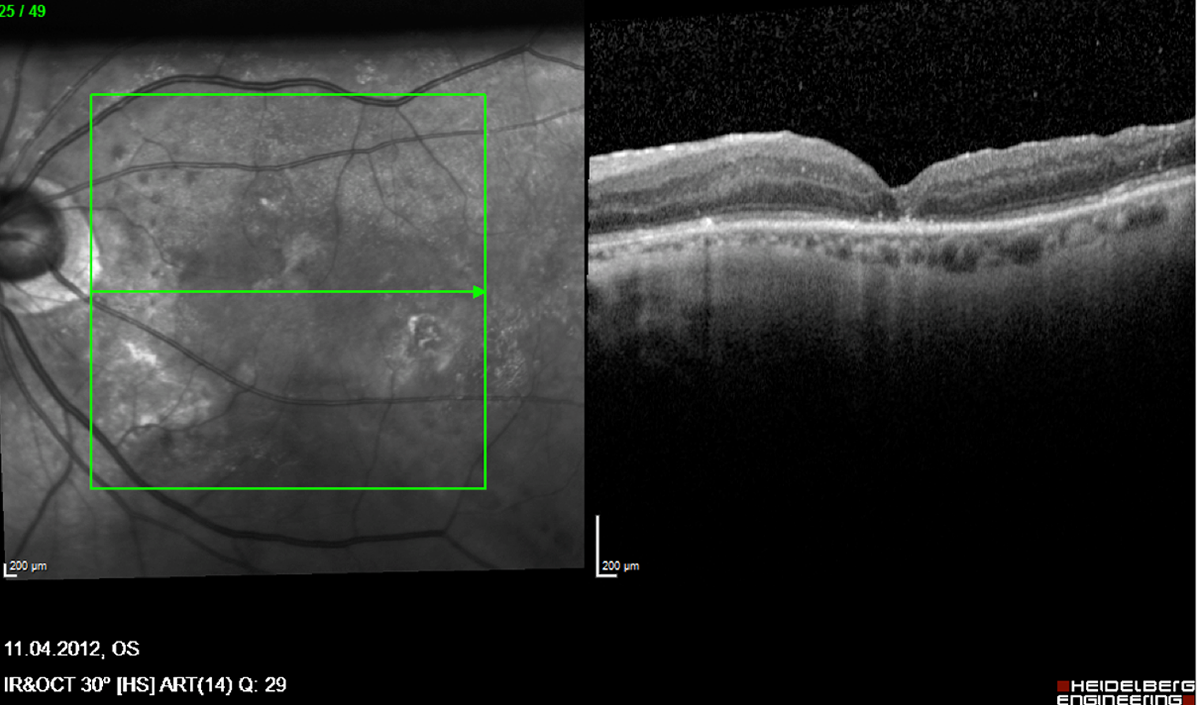
Picture 1: Macular hole before surgery
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF A MACULAR HOLE ?
In the early stages of macular hole formation, symptoms may not be completely obvious. Your central vision becomes blurred and distorted. If the hole progresses, a blind spot develops in your central vision and impairs the ability to see at both distant and close range. Symptoms of macular hole usually occur in one eye only, as it is uncommon to have a macular hole in both eyes.
Macular hole symptoms include:
- Decreased ability to see fine details when looking directly at something at any distance;
- Vision distortion similar to looking through thick fog or wavy glass.
- A dark or blind spot in the center of the field of vision.
If any of these symptoms occur, it is important to schedule an appointment with your eye doctor as soon as possible. Your ophthalmologist will use a special instrument to look inside the eye and see whether the macula has a hole in it.
It is important to note that if the macula is damaged, you will not lose your vision entirely. You will still have peripheral, or side, vision.

HOW CAN WE DIAGNOSE A MACULAR HOLE ?
During an eye exam, your ophthalmologist will dilate your pupils and examine your retina. You may have a test called fluorescein angiography that uses dye to illuminate areas of the retina.
Another test called optical coherence tomography (OCT) is most helpful in making an accurate macular hole diagnosis. With OCT, a special diagnostic laser camera is used to photograph your retina. It measures the thickness of the retina and is also very sensitive at detecting swelling and fluid. OCT can also diagnose small macular holes that are too small to be seen in an examination or with angiography.
Picture 2: Macular hole after surgery
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR A MACULAR HOLE ?
Macular hole surgery involves using tiny instruments to remove the vitreous gel that is pulling on the macula. The eye is then filled with a special gas or oil bubble to help flatten the macular hole and hold the retinal tissue in place while it heals.

In the face-down position, the bubble is in contact with macula
If you have vitrectomy surgery, you must maintain a constant face-down position after surgery to keep the bubble in contact with the macula to allow effective healing. This can range from a few days to a few weeks, depending on your surgeon’s recommendation and the size of your hole. A successful result often depends on how well this position is maintained. The bubble will then slowly dissolve on its own, or, in some cases, be removed by your ophthalmologist.
If you have a gas bubble, you cannot fly in an airplane until the gas bubble has dissolved, as a rapid increase in altitude can cause a dangerous rise in eye pressure. You must also not undergo general anesthesia using nitrous gas, though it is generally safe to have general anesthesia without using nitrous gas.
As the macular hole closes, the eye usually regains some of the lost sight. How much vision is restored generally depends on the size of the hole and how long it was present before surgery.






